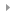DRYER
(Essential for wet coating)

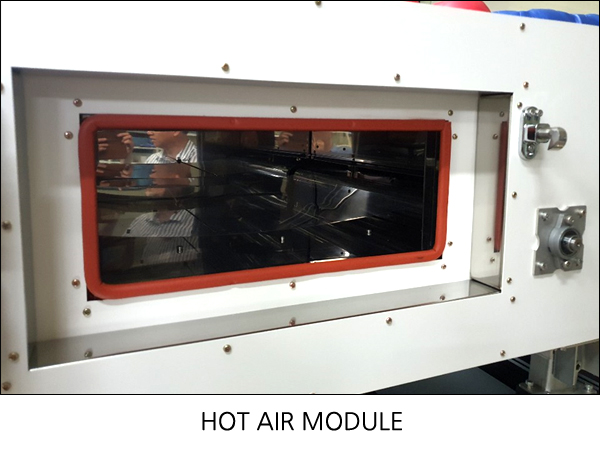
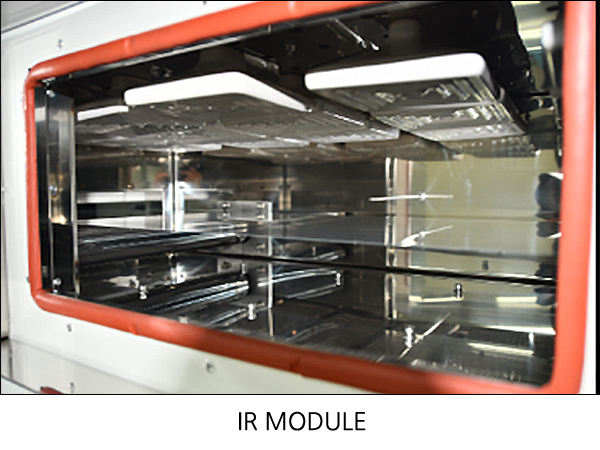
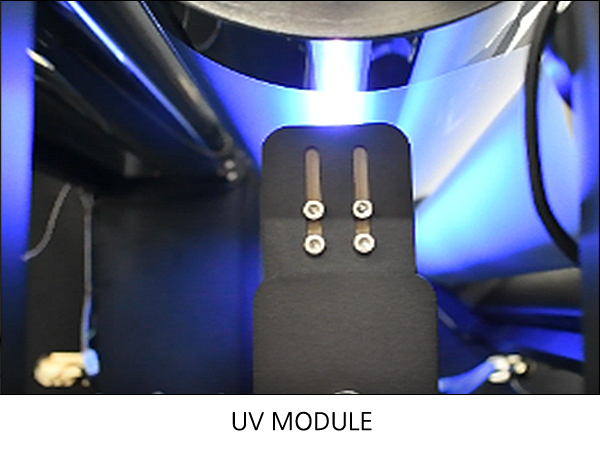
[ Drying technology ] Technology that thins materials in a liquid state during the wet process and a drying process required during the wet coating. Drying devices can be roughly divided into hot air drying, IR drying, and drying using UV. A mixed structure combining these can be designed according to the drying process and the properties of the material. The technology required for the dryer is as follows: - Uniform temperature and air speed - Cleaning of internal atmosphere - Stable operating performance, suppression of dry trouble - Energy saving |
[ Features ] - PID control per each zone temperature - Derivation of the best drying method according to material and system optimization - IR Lamp arranges ceramic heaters in a lattice structure to ensure uniform heat distribution - Smooth hot air fume discharge in the chamber and prevents internal pollution - Supplying particle-free clean hot air using a high-temperature HEPA filter - Max. 150 ℃ (hot air), max. 400 ℃ (IR), 360 ~ 410nm (UV) |
Temperature stability and control
|
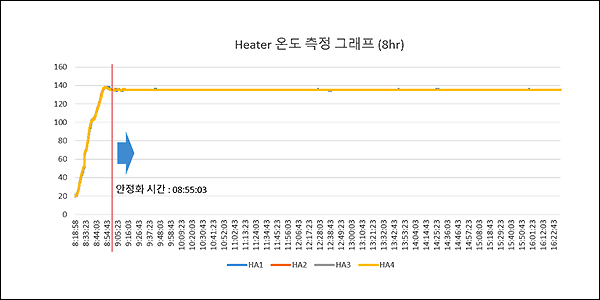
[ Features ] - Temperature deviation after stabilization: 135 ℃ ±1℃ - WEB left/right temperature deviation: 135 ℃ ± 2.3 % - Complexation of heat wind and IR ceramic, if necessary - Application of supply/exhaust and overcurrent monitoring and block |
|
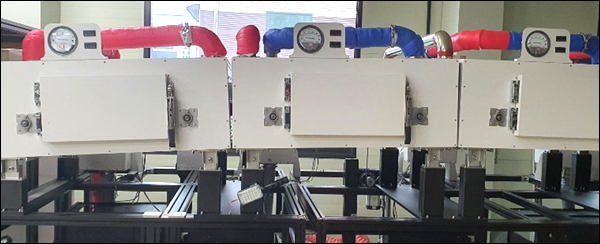
[ Temperature measurement graph ] - Atmosphere temperature measurement of each drying zone by sensor - Temperature deviation after target temperature stabilization (135℃ ±1℃)) |
- Web surface temperature left/right deviation test for all drying zones (135 ℃ ± 2.3%)
Turning liquid into a thin film during the wet process. (Essential for wet coating)



[ Drying technology ]
Technology that thins materials in a liquid state during the wet process and a drying process required during the wet coating.
Drying devices can be roughly divided into hot air drying, IR drying, and drying using UV. A mixed structure combining these can be designed according to the drying process and the properties of the material.
The technology required for the dryer is as follows:
- Uniform temperature and air speed
- Cleaning of internal atmosphere
- Stable operating performance, suppression of dry trouble
- Energy saving
[ Features ]
- PID control per each zone temperature
- Derivation of the best drying method according to material and system optimization
- IR Lamp arranges ceramic heaters in a lattice structure to ensure uniform heat distribution
- Smooth hot air fume discharge in the chamber and prevents internal pollution
- Supplying particle-free clean hot air using a high-temperature HEPA filter
- Max. 150 ℃ (hot air), max. 400 ℃ (IR), 360 ~ 410nm (UV)
Temperature stability and control
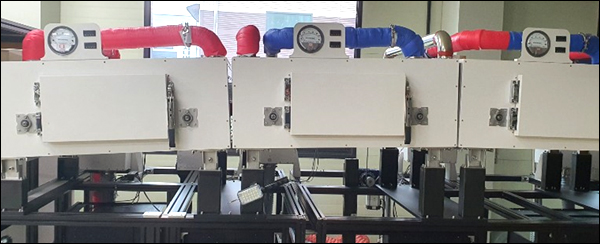
[ Features ]
- Temperature deviation after stabilization: 135 ℃ ±1℃
- WEB left/right temperature deviation: 135 ℃ ± 2.3 %
- Complexation of heat wind and IR ceramic, if necessary
- Application of supply/exhaust and overcurrent monitoring and block
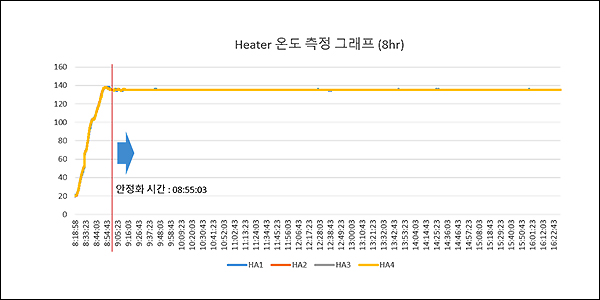
[ Temperature measurement graph ]
- Atmosphere temperature measurement of each drying zone by sensor
- Temperature deviation after target temperature stabilization (135℃ ±1℃)
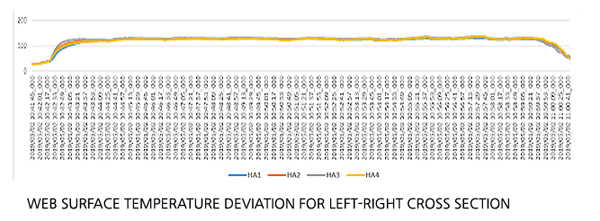
- Web surface temperature left/right deviation test for all drying zones (135 ℃ ± 2.3%)
Turning liquid into a thin film during the wet process. (Essential for wet coating)



[ Drying technology ]
Technology that thins materials in a liquid state during the wet process and a drying process required during the wet coating.
Drying devices can be roughly divided into hot air drying, IR drying, and drying using UV. A mixed structure combining these can be designed according to the drying process and the properties of the material.
The technology required for the dryer is as follows:
- Uniform temperature and air speed
- Cleaning of internal atmosphere
- Stable operating performance, suppression of dry trouble
- Energy saving
[ Features ]
- PID control per each zone temperature
- Derivation of the best drying method according to material and system optimization
- IR Lamp arranges ceramic heaters in a lattice structure to ensure uniform heat distribution
- Smooth hot air fume discharge in the chamber and prevents internal pollution
- Supplying particle-free clean hot air using a high-temperature HEPA filter
- Max. 150 ℃ (hot air), max. 400 ℃ (IR), 360 ~ 410nm (UV)
Temperature stability and control

[ Features ]
- Temperature deviation after stabilization: 135 ℃ ±1℃
- WEB left/right temperature deviation: 135 ℃ ± 2.3 %
- Complexation of heat wind and IR ceramic, if necessary
- Application of supply/exhaust and overcurrent monitoring and block

[ Temperature measurement graph ]
- Atmosphere temperature measurement of each drying zone by sensor
- Temperature deviation after target temperature stabilization (135℃ ±1℃)


- Web surface temperature left/right deviation test for all drying zones (135 ℃ ± 2.3%)